Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome is the occurrence of fluid leaking from the bloodstream and building up into small and stretchy sacks known as alveoli within one’s lungs. As the fluid continues to build up within these sacks, the sacks grow leaving less room within the lungs for air to get to. This makes it harder for one to breath making it harder for oxygen to make it into the bloodstream. This causes deprivation of oxygen for organs that require it. Most people do not end up surviving this fatal disease.
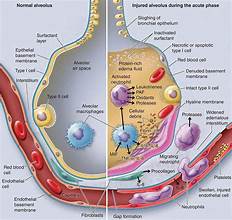
Gaps will start forming within the Endothelial Basement Membrane causing Neutrophils to enter and platelets to form in the bloodstream. The Hyaline forms in place of the Type 1 cell. Due to the Hyaline, Fibrin starts to form and ends up causing cellular debris to form. Red Blood Cells end up escaping the stream and entering the alveoli. Due to the lack of protection, both bacteria and a protein rich edema fluid starts to form. As this grows the lungs end up lacking space to breath air leaving a lack of oxygen.
ARDS usually forms within people who are critically ill or have significant injuries. Symptoms usually include shortness of breath, rapid breathing, low blood pressure, and confusion/extreme tiredness. The most common causes include Sepsis, inhalation of harmful substances, severe pneumonia, head or chest or any other major injuries, coronavirus, inflammation of the pancreas, massive blood transfusions, and even burns. Many people who develop this condition don’t end up surviving. Some people end up surviving and either fully recovering or experience long lasting effects on their lungs.
People who are critically ill are at a high risk for ARDS. Other risk factors include severe alcoholism, and people who intake harmful substances like vaping and smoking. Common side effects include blood clots, Pneumothorax (Collapsed lung), infections, and Pulmonary fibrosis (scarring). Luckily we are at a point in time where people can improve their health after ARDS. Common effects after ARDS include breathing problems, depression, issues with memory, and tiredness within the muscle.
1.) MesenCure by Bonus BioGroup for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Likelihood of Approval – MesenCure are currently coming up with a cure for ARDS and right now contain a 31% chance of a success rate. These tests are administered through transfusions. The medication contains mesenchymal stromal cells which reside within the adipose tissue.
2.) $3.4 million grant awarded to identify therapeutic treatments for acute respiratory distress syndrome – UTHealth Housten was awarded $3.4 million for discovering molecular mechanisms and therapeutic treatments for ARDS. Investigator Holger Eltzschig, the Department Anesthesiology, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, and Xiaoyi Yuan have performed studies on ARDS and methods to possibly reduce ARDS’s affects. Therapeutic strategies aren’t always brought up when at clinics reducing the possible ways to help reduce ARDS.
3.) Medical Moment: Unraveling the mysteries of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome – Effective treatments are very hard to come by and discover. It’s so hard to discover new ways to help patients with ARDS due to the different ways people react to it. Antibiotics usually only help 50% of patients recover from ARDS.
- “MesenCure by Bonus BioGroup for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome” pharmaceutical-technology.com https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/uncategorized/mesencure-bonus-biogroup-acute-respiratory-distress-syndrome-likelihood-of-approval-2/
- “$3.4 million grant awarded to identify therapeutic treatments for acute respiratory distress syndrome” news-medical.net https://www.news-medical.net/news/20231026/2434-million-grant-awarded-to-identify-therapeutic-treatments-for-acute-respiratory-distress-syndrome.aspx
- “Medical Moment: Unraveling the mysteries of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome” wndu.com https://www.wndu.com/2023/10/18/medical-moment-unraveling-mysteries-acute-respiratory-distress-syndrome/