What is Riboflavin Deficiency?
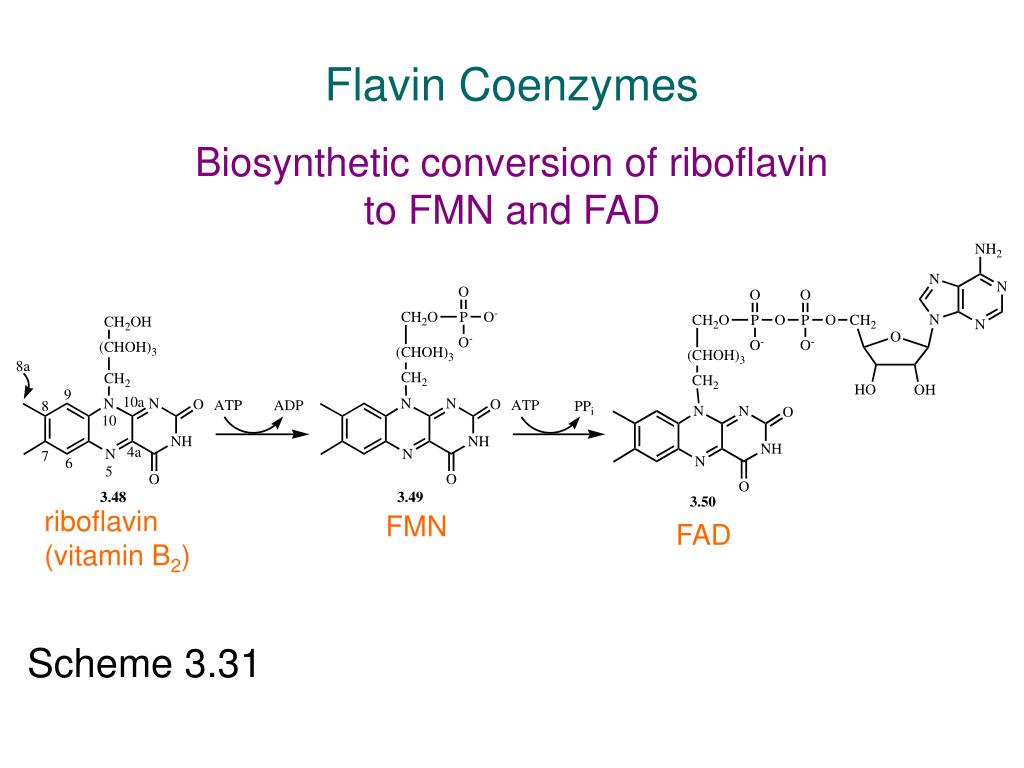
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in energy metabolism, cellular respiration, antibody production, and overall normal growth and development (Lefton, 2023).
B2 is found in many major food sources such as meat, dairy, eggs, and leafy greens. Riboflavin, like any other vitamin deficiency, can cause a host of issues all over the body which can make deficiencies hard to track. Issues can range anywhere from skin disorders like dermatitis, especially around the nose, ears, and mouth to nerve damage. Although rare, it can occur in serious cases of B2 deficiency. B2 deficiency can be prevented by proper diets and oral supplementation.
Development of Riboflavin Deficiency
Common causes and prevention
There are two main reasons why people experience B2 deficiencies. Poor diets and conditions that may inhibit the absorption of riboflavin. One example is simply not consuming foods with riboflavin. Lifestyle choices like veganism can take away many important foods that are rich in vitamins required for your body to function. Psychological conditions like anorexia nervosa, bulimia, and alcoholism can also affect riboflavin levels. Another factor that causes riboflavin deficiency is not only failure of consuming enough of it, but the body itself not being able to absorb riboflavin when consumed. Many conditions can cause the body to inadequately absorb molecules responsible for body function. Common examples are digestive disorders like chrons disease and malabsorption syndromes like cystic fibrosis.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis
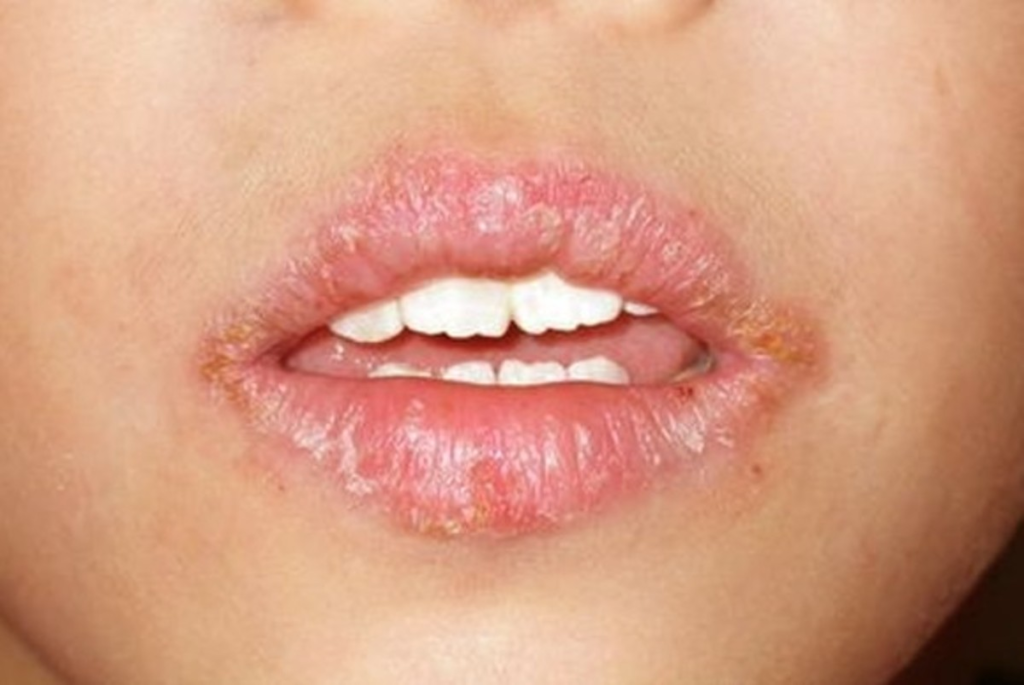
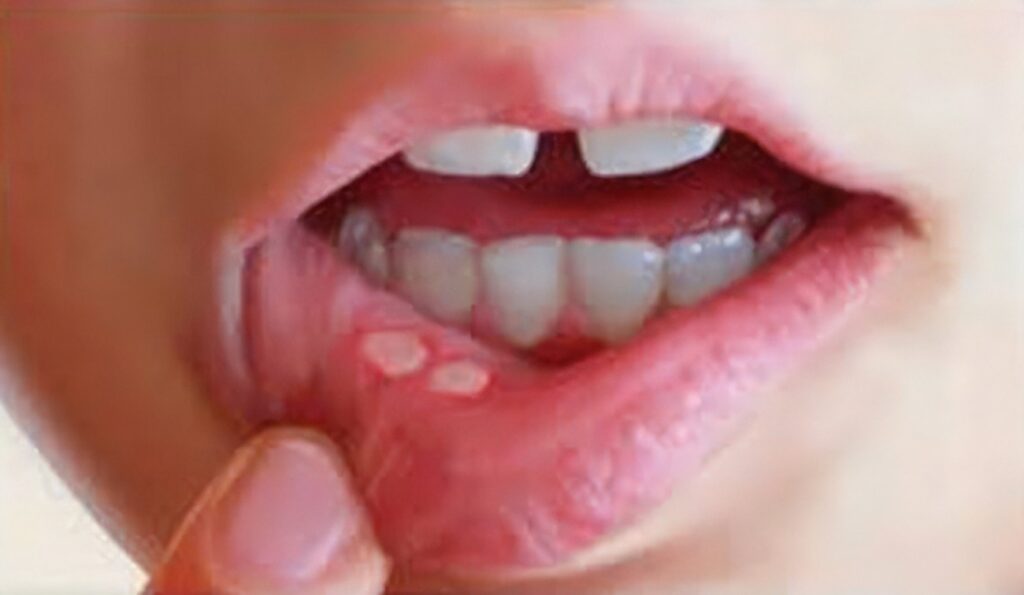
As stated previously, riboflavin deficiency, and many other vitamin deficiencies, are intractable due to all its odd symptoms it can present. Doctors use a multilayer system to identify root issues. Most likely, practitioners will start with medical history and physical examination. Doctors will ask about symptoms, dietary habits, supplementations, medications, and medical history. This can rule out other possible causes to the noticeable physical changes associated with riboflavin deficiency. In some cases, doctors will utilize a function or blood test of the vitamins in your blood stream to pin-point exact vitamins. There are a lot of noticeable physical changes that can present themselves: Cheilosis, Stomatitis, Glossitis, pale skin, and greasy or itchy skin, specifically around the scrotum for men or the labia majora for women.
Some noticeable mental changes associated with this deficiency is mental fatigue, confusion, and sluggishness. In serious cases, riboflavin deficiency can cause dysfunction between the nerves and nerve damage. Again, it is crucial to reiterate that nerve damage is quite rare with riboflavin deficiency but must be treated seriously. Nerve damage can present in numerous forms: Loss of coordination, burning sensations, weakness, altered sensations, and in severe nerve damage cases, muscle atrophy.
Treatment
Treatment is quite simple. Depending on the reasoning behind the deficiency like failure of consuming foods rich in riboflavin, doctors will simply prescribe oral supplements to help restore levels of riboflavin. If the reasoning behind the deficiency is related to the body’s failure to simply absorb nutrients, doctors will first identify the underlying cause than asses several different methods to see which one will be the most effective treatment option for that patient. Some of these methods of treatment include:
- Supplementation: Doctors may prescribe vitamin supplements to ensure the patient receives adequate amounts of the deficient vitamins. These supplements are often in higher doses than what is typically found in over-the-counter supplements.
- Intravenous (IV) Therapy: In severe cases where oral supplements are not sufficient, vitamins may be administered intravenously to bypass the digestive system. Intravenous, the most common method, is where nutrients are specifically administered through a vein, but other methods include:
- Intramuscular (IM) injections are administered into a muscle.
- Subcutaneous (SC) injections are given just beneath the skin.
- Intradermal (ID) injections are placed just under the epidermis (outer layer of the skin).
Published Articles
B Vitamins: Your Secret to Good Skin Health – Tri-City Medical Center (tricitymed.org.
This article discusses the benefits of the vitamin B complex for the skin. Many symptoms of vitamin B deficiency root in skin conditions. Here is a complete list of the entire B vitamin complex and the benefits of each vitamin.
Riboflavin – Health Professional Fact Sheet (nih.gov)
This article specifically discusses the complications of riboflavin deficiency in infants. Pregnant or lactating women who rarely consume meats or dairy products (such as those living in developing countries) are at risk of riboflavin deficiency.
Can a Vitamin Deficiency Cause Fungal Infections? (healthline.com)
This article explores the concepts of antifungal properties of B and D vitamins. It also explains the link between compromised immune systems and increased risk due to vitamin B deficiency.
References
“Vitamin B Deficiency: Your Complete Guide”; Forbes.com; Vitamin B Deficiency: Your Complete Guide – Forbes Health
“Benefits and Sources of Vitamin B2”; MedicalNewsToday; Vitamin B2: Role, sources, and deficiency (medicalnewstoday.com)
“Riboflavin Deficiency”; National Library of Medicine; Riboflavin Deficiency – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
“Riboflavin Deficiency”; MSD Manual; Riboflavin Deficiency – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
Lefton. J (2023, June 20) “Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Everything You Should Know”;VeryWell Health; Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Benefits, Deficiency, and More (verywellhealth.com)