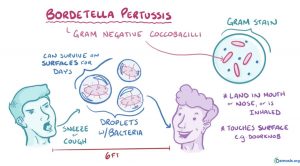
Whooping Cough is a bacterial infection that affects your nose and throat. Many may also know it as Pertussis. Bordetella Pertussis is the bacteria responsible for this contagious infection. Some of the symptoms include coughing, sneezing, fever and many more. The reason it was named Whooping Cough is because it is a infection that produces many coughing episodes, but there is no mucus produced when coughing. There have been many outbreaks of the infection due to a failure of the vaccine.
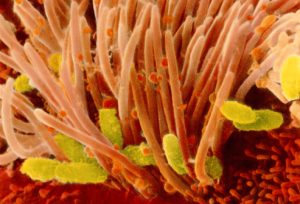
B. Pertussis bacteria attaches to your cilia in your respiratory system, which are little hairs in your respiratory pathway that helps move mucus. Once attached the bacteria releases toxins causing the cilia to paralyze. The toxins released cause your airway to swell making it hard to breath. Swollen airways result in the “whooping” sound that one produces during these coughing episodes. Mucus is not produced due to the cilia being unable to move, which results in a dry cough. After being diagnosed it is important to stay away from any cough medicine. Cough medicine helps you cough mucus out of the airway. Since you do not produce any mucus to cough up, cough medicine could just make it worse.
Whooping Cough can be deadly in some cases. It is important you get to a doctor when experiencing any of the symptoms (sneezing, coughing, low fever, diarrhea, and stuffy nose). Vaccine(s) DTap and Tdap are used to help prevent one from getting the infection. These vaccines are required to stop the nationwide spread of Pertussis. When you are diagnosed with the infection, antibiotics can be prescribed to speed up your recovery time. This infectious bacteria can be extremely harmful for infants and toddlers. In adults, Whooping Cough can make it hard to breath. Pertussis makes children severely breathless, which could result in death.
In the United States, whooping cough had a huge increase over the years. In 1934 there was a report of over 200,000 Americans that had this Infection. Once the vaccine was founded the reports went down to 1,000 in 1976. Today many who report having the infection also had the vaccine. Researchers believe the increase is a result of the vaccine DTap failing. In 2013 there were many cases of Whooping Cough and many people blaming one another. As of 2018 many realize DTap is not working and no one is to blame for the spread of the virus. Overall, Pertussis can be easily contracted and when it is it can be very harmful.
“Everyday Health, 10 Essential Facts About Whooping Cough, Pertussis”; EverydayHealth.com; https://www.everydayhealth.com/news/10-essential-facts-about-whooping-cough/
“Whooping Cough: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention” ; WebMD.com; https://www.webmd.com/children/whooping-cough-symptoms-treatment#1
“Pertussis | Whooping Cough | Causes and Transmission | CDC” ; CDC.gov; https://cdc.gov/pertussis/about/causes-transmission.html
“Whooping Cough Outbreaks Continue Nationwide Due to Failed Pertussis Vaccine” ; thevaccinereaction.org; https://thevaccinereaction.org/2018/06/whooping-cough-outbreaks-continue-nationwide-due-to-failed-pertussis-vaccine/