Variola Virus is also known as Smallpox, this is a very rare disease. Smallpox has two main virus categories, Variola Major and Variola Minor. Both major and minor produce similar symptoms and lesions. Naturally occurring smallpox was eradicated in 1980. This virus spreads very quickly and its symptoms include flu-like symptom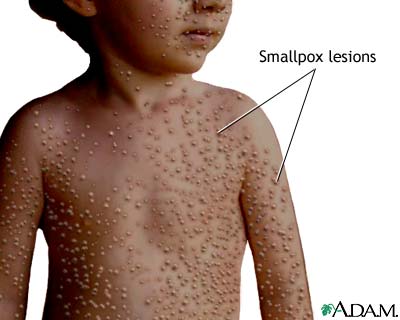 s and a rash occurring over multiple regions of the body. At this time there is no treatment for the Variola Virus
s and a rash occurring over multiple regions of the body. At this time there is no treatment for the Variola Virus
| Formal binomial name of microbe: | Orthopoxvirus variola |
| Gram stain (gram positive, gram negative or neither): | Neither |
| Is the microbe mobile or immobile? | Immobile |
| Primary habitat? (Where is the organism normally found or prefer to live?) | Reservoir is humans with the disease |
| Can the organism infect humans? | Yes |
| Can the organism infect other species? If so, which ones. | No |
| Documented cases of antimicrobial resistance? | Yes-resistant to all antimicrobials |
| Number of infections per year in the US | No naturally occurring outbreaks in the U.S since 1949 |
| Number of infections per year in the world | 1978 last case of smallpox in the world |
Pathogenic Profile: Smallpox is a highly contagious disease caused by a double-stranded DNA that is enveloped. Variola Major is the cause of more deadly cases of smallpox in comparison to Variola Minor. Minor produces very mild symptoms that are not life-threatening however Variola Minor is a much less common than Major.
Mode of Transmission: The natural reservoir for smallpox is the human with the disease. The usual entry point of the virus into the body is through the respiratory system. This happens generally through coughing. People are most contagious during the first week of the rash that appears on their face, hands, and trunk. It can also be transmitted through skin to skin contact of a skin lesion or infected body fluids. Smallpox is highly infectious and its infection dose is very small, making this disease very easy to infect a person even in the presence of only a few droplets.
contagious during the first week of the rash that appears on their face, hands, and trunk. It can also be transmitted through skin to skin contact of a skin lesion or infected body fluids. Smallpox is highly infectious and its infection dose is very small, making this disease very easy to infect a person even in the presence of only a few droplets.
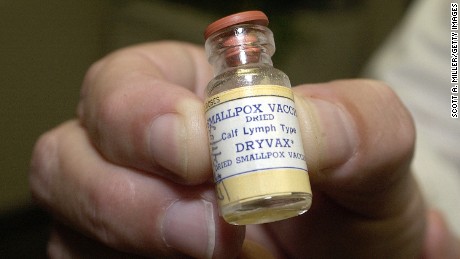
Vaccination: The last recorded smallpox infection in the U.S was in 1949. During that time, everyone was routinely receiving smallpox vaccines. In 1971 the risk of smallpox was so low that they stopped routine vaccinations. Only select populations are required to receive the vaccination. All military personnel are required to receive the smallpox vaccine and as of 2002, select healthcare workers and emergency responders are required to receive the vaccine.
Smallpox in the News
Preparing for Smallpox Outbreak: Public Health Dept in Missouri has set up a mass vaccination training in the case of a smallpox outbreak. In 2014, 6 vials of smallpox we found in a box in a Washington research center.
Post-Exposure Prophalytic for Smallpox: SIGA, a commercial pharmaceutical company was granted a multi-million dollar budget by the United States Dept of Defense. The hope is to expand and manufactureTPOXX, a post-exposure prophylactic.
Smallpox, The World’s First Eradicated Disease: An estimated 300 million lives were lost due to smallpox in the 20th century. The first smallpox vaccination was produced in 1796, but it took over 200 years before the vaccine was made a part of routine healthcare and eventually eradicated the disease.
References
“Health Department Trains for Smallpox Outbreak”; columbiatribune.com; https://www.columbiatribune.com/news/20190208/health-department-trains-for-smallpox-outbreak
“Pathogen Profile Dictionary: Smallpox Virus”; ppdictonary.com; https://www.ppdictionary.com/viruses/smallpox.htm
“SIGA Awarded Department of Defense Contract to Develop Expanded Indication for TPOXX as Post-Exposure Prophalytic for Smallpox”; globnewswire.com; https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2019/07/08/1879366/0/en/SIGA-Awarded-Department-of-Defense-Contract-to-Develop-Expanded-Indication-for-TPOXX-as-Post-Exposure-Prophylactic-for-Smallpox.html
“Smallpox”; sfcdcp.org; https://www.sfcdcp.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/Smallpox-Binder-Chapter.2008.FINAL-id314.pdf
“Smallpox”; cdc.gov; https://www.cdc.gov/smallpox/index.html
“Smallpox: The World’s First Eradicated Disease”; livescience.com; https://www.livescience.com/65304-smallpox.html
